A* is based on using heuristic methods to achieve optimality and completeness, and is a variant of the best-first algorithm. Each time A* enters a state, it calculates the cost, f(n) (n being the neighboring node), to travel to all of the neighboring nodes, and then enters the node with the lowest value of f(n). These values are calculated with the following formula:
g(n) being the value of the shortest path from the start node to node n,
and h(n) being a heuristic approximation of the node's value.
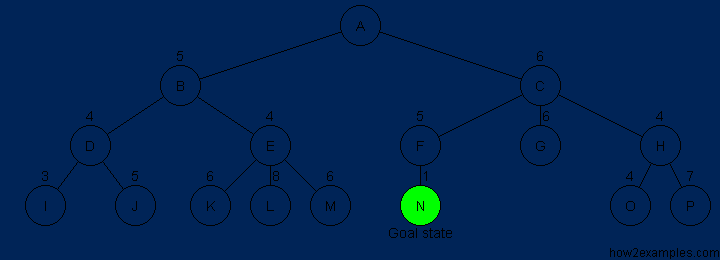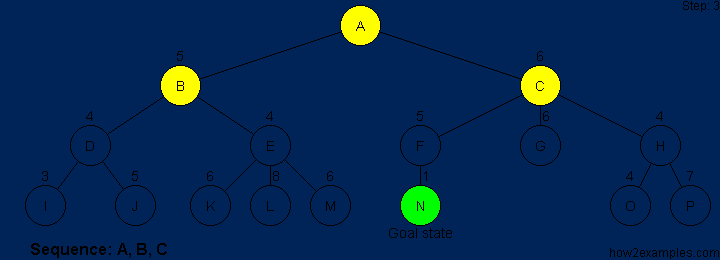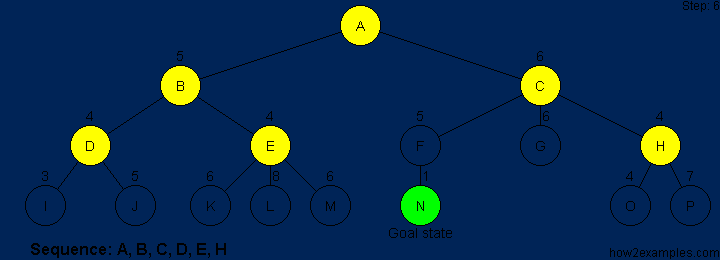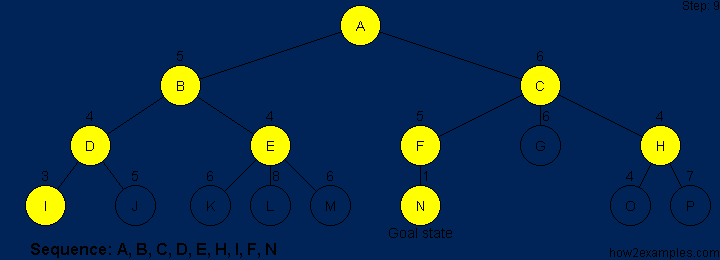
The efficiency of A* is highly dependent on the heuristic value h(n),
and depending on the type of problem,
we may need to use a different heuristic function for it to find the optimal solution.