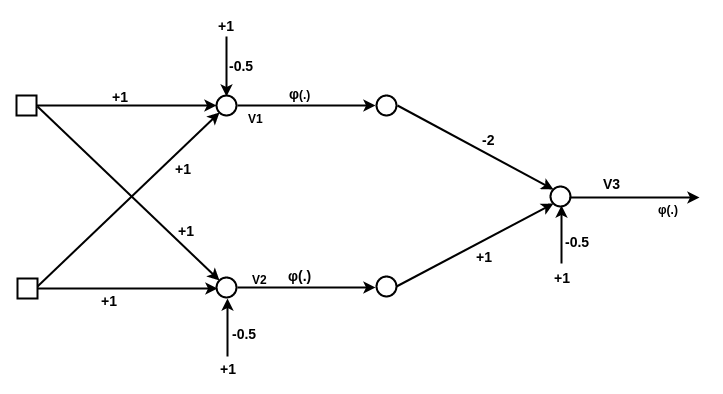
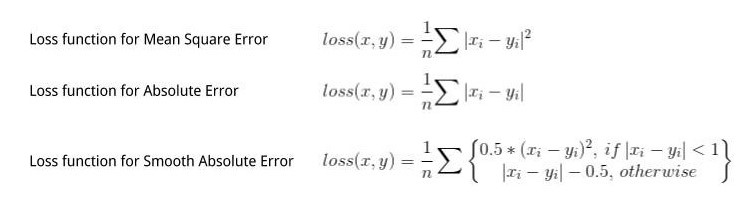A multilayer perceptron (MLP) is a deep, artificial neural network.
It is composed of more than one perceptron.
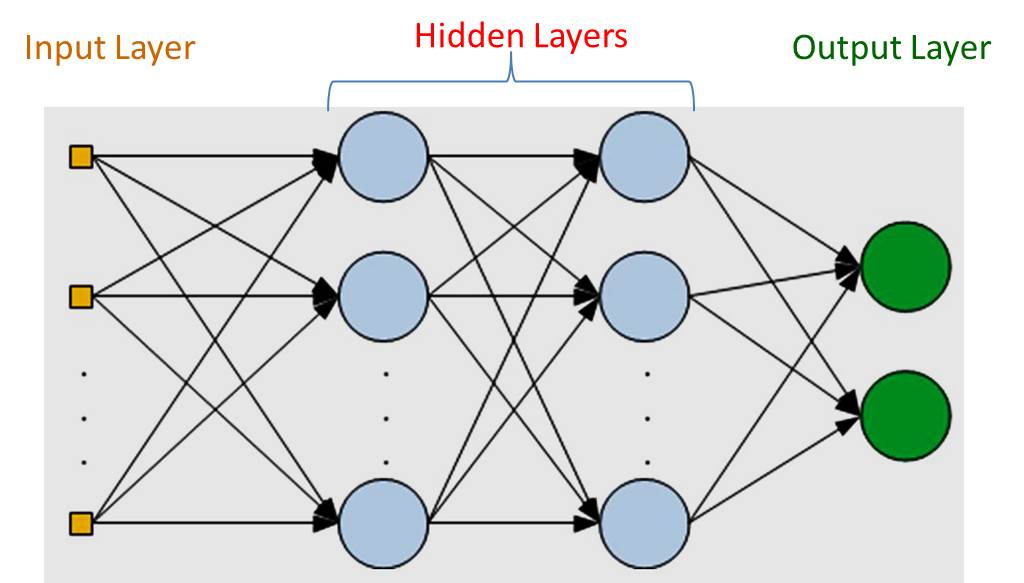
They are composed of an input layer to receive the signal, an output layer that makes a decision or prediction about the input,
and in between those two, an arbitrary number of hidden layers that are the true computational engine of the MLP.
MLPs with one hidden layer are capable of approximating any continuous function.
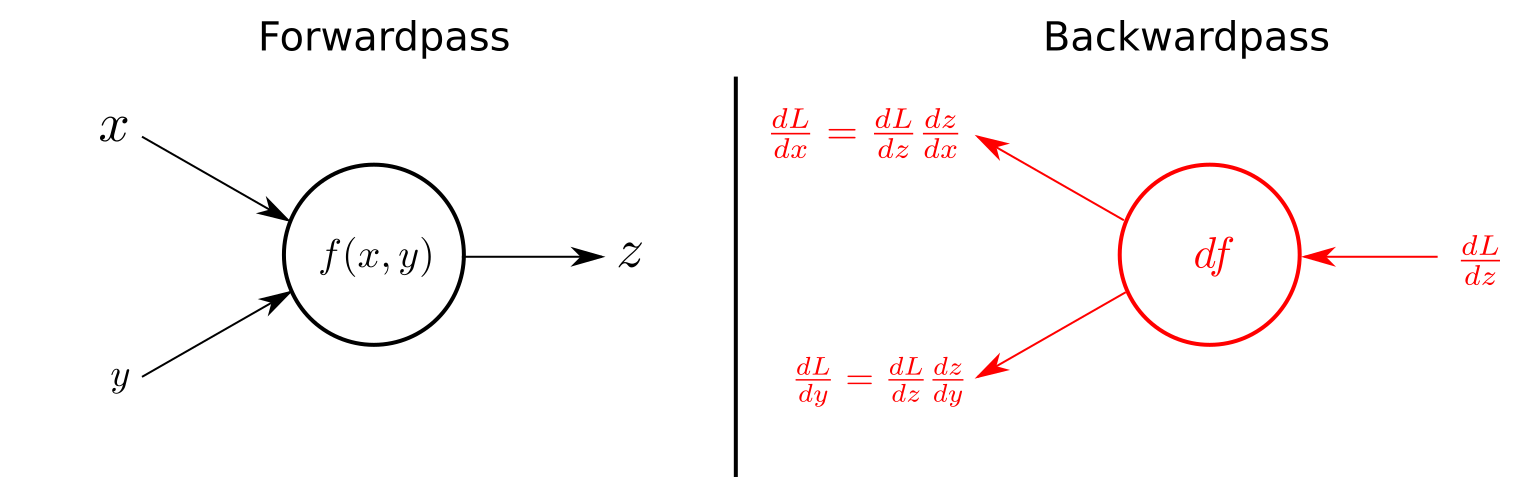
Multilayer perceptrons are often applied to supervised learning problems: they train on a set of input-output pairs and learn to model the correlation (or dependencies) between those inputs and outputs. Training involves adjusting the parameters, or the weights and biases, of the model in order to minimize error. Backpropagation is used to make those weigh and bias adjustments relative to the error, and the error itself can be measured in a variety of ways, including by root mean squared error (RMSE).